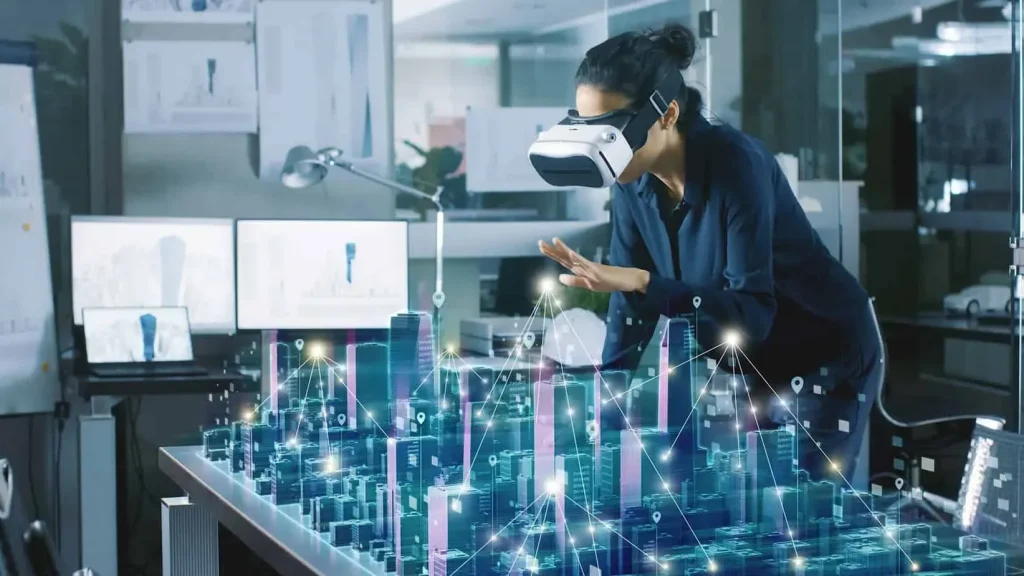
Augmented Reality and VR breakthroughs are reshaping how industries operate, turning futuristic concepts into practical tools that help teams visualize data, collaborate across distances, and act with confidence when every move counts, whether on the factory floor, in a hospital corridor, or out in the field. Across sectors from manufacturing to healthcare, these technologies are moving beyond novelty to become core drivers of productivity, safety, and learning, with real-world progress illustrated by augmented reality applications in industry that guide workers through complex steps with hands-free precision and timely feedback. In the realm of operations, AR training and remote assistance enable rapid upskilling and expert support without travel, letting seasoned technicians annotate live equipment views, share step-by-step guidance, and provide actionable insights as teams work through challenging procedures. The technology stack—the combination of lightweight wearables, sensors, edge computing, and AI-powered analytics—creates a platform where real-world contexts are enriched with overlays, predictive cues, and safety checks that help reduce downtime and improve quality. As adoption accelerates, leaders are designing scalable programs that align immersive experiences with measurable outcomes, investing in user-friendly interfaces, governance, and change-management practices so these tools become trusted partners rather than disruptive gadgets.
From a Latent Semantic Indexing perspective, the conversation around AR and VR breakthroughs shifts toward related concepts such as mixed reality, immersive environments, and digital overlays that sit at the center of usability and value. In practical terms, analysts describe experiences with MR, spatial computing, and holographic interfaces to convey how digital content becomes a real-time extension of the user’s workspace. This framing enhances content discoverability by linking design reviews, training simulations, and remote collaboration, guiding readers to adjacent topics without losing coherence. As teams operate in shared virtual spaces, data from enterprise systems can be woven into immersive workflows, enabling better decision-making, faster iterations, and safer, more compliant routines. Beyond the factory and clinic, the same language supports education, maintenance, and field operations by spotlighting immersive technology for education and other value propositions that resonate with diverse audiences. In short, framing technology in this way makes content more navigable, relevant, and practical—reflecting the real-world outcomes that organizations seek as they adopt AR and VR at scale.
Augmented Reality and VR breakthroughs: Transforming industry workflows
Augmented Reality and VR breakthroughs are redefining how work gets done across industries. The convergence of lightweight wearable devices, edge computing, high-bandwidth networks, and AI-driven analytics enables near real-time digital overlays that guide decisions, improve safety, and shorten cycle times. As a result, teams move beyond novelty demos toward durable improvements in productivity and quality.
These breakthroughs are fueling broader adoption across the enterprise, with augmented reality applications in industry moving from pilots into mission-critical workflows. By presenting contextual data at the point of action, workers can perform complex tasks with fewer errors, while leaders gain visibility into performance and compliance. AR training and remote assistance extend expert reach to the frontline, accelerating ramp-up and reducing downtime.
AR applications in industry: Real-time guidance on the factory floor
AR applications in industry are enabling real-time guidance on factory floors. Workers receive hands-free, step-by-step instructions that align with assembly sequences, poka-yoke checks, and quality-control steps, all delivered through intuitive overlays that do not block vision and allow seamless task execution.
In field service, technicians wear AR glasses that stream equipment sensor data, display repair manuals in context, and allow remote experts to annotate the live view. This capability reduces travel time, speeds maintenance, and improves first-time fix rates.
VR breakthroughs in manufacturing: from prototyping to virtual commissioning
VR breakthroughs in manufacturing empower engineers to prototype processes, test ergonomics, and validate workflows in a risk-free digital environment before a single physical component is built. Digital twins and high-fidelity simulations enable rapid iteration, reduce waste, and shorten time-to-market.
Collaborative design reviews become more inclusive as dispersed teams meet in shared virtual spaces to explore options, compare layouts, and converge on decisions without travel. VR-driven testing accelerates validation and helps stakeholders align on specifications early, lowering project risk.
AR and VR in healthcare: Safer procedures and patient education
In healthcare, AR overlays assist in planning surgeries, visualize radiology data in context, and guide invasive procedures with real-time cues. The combination of AR and VR in healthcare supports safer procedures, more accurate planning, and enhanced patient education through immersive visuals.
Hospitals also deploy VR for pain management, exposure therapy, and rehabilitation, while surgeons experiment with patient-specific simulations and augmented planning tools. Across care settings, these technologies improve training efficiency and help clinicians practice complex scenarios without risk to patients.
AR training and remote assistance: Empowering frontline workers
AR training and remote assistance reshape onboarding and ongoing skill development by embedding contextual guidance into real work. New hires learn by doing with overlays that appear exactly where the action takes place, accelerating proficiency and reducing errors.
On the maintenance floor and in field service, remote experts annotate live views, provide guidance, and troubleshoot in real time. This model lowers downtime, boosts first-time fix rates, and makes scarce expertise scalable across sites.
Immersive technology for education: Scaling hands-on learning with AR/VR
Immersive technology for education makes abstract concepts tangible through interactive simulations, virtual labs, and scenario-based practice. Students in STEM and vocational tracks gain practical experience even when access to physical facilities is limited.
It also enables safe, cost-effective training outside traditional classrooms, supports remote learning, and opens up new pathways for equipping teachers with engaging tools. As immersive education matures, schools and training programs will be better positioned to prepare a diverse workforce for the demands of modern industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are augmented reality applications in industry, and how are they transforming maintenance and assembly workflows?
Augmented reality applications in industry overlay digital guidance onto the real world, enabling hands-free, real-time instructions during maintenance and assembly. By showing step-by-step overlays, safety cues, and live data from sensors, AR reduces errors, speeds up training, and lowers downtime, especially on busy factory floors and in logistics. Successful deployments rely on lightweight devices, reliable data feeds, and integration with existing systems.
What do VR breakthroughs in manufacturing mean for production lines, design reviews, and operator training?
VR breakthroughs in manufacturing enable high-fidelity simulations and digital twins of production lines, allowing designers and operators to prototype processes, test ergonomics, and conduct virtual commissioning before any physical build. This shortens development cycles, improves safety, and accelerates stakeholder alignment through immersive design reviews and cross-team collaboration.
How are AR and VR in healthcare changing surgical planning, training, and patient care pathways?
AR and VR in healthcare blend real-world imagery with virtual planning tools to enhance surgical planning, radiology workflows, and patient education. VR provides realistic simulations for training and rehabilitation, while AR overlays assist in the operating room or planning stages, improving precision, safety, and confidence among care teams.
How does AR training and remote assistance accelerate onboarding, field service productivity, and knowledge transfer?
AR training and remote assistance accelerate onboarding by delivering context-aware instructions in the workflow, reducing time-to-competence and the risk of errors. On field service, technicians access manuals, live sensor data, and expert annotations without leaving the job site, improving first-time fix rates and uptime.
How is immersive technology for education enabling safer, more accessible hands-on learning in classrooms and remote settings?
Immersive technology for education uses interactive simulations, virtual labs, and situated scenarios to make complex concepts tangible. It broadens access to high-quality instruction, supports remote and under-resourced settings, and improves engagement, collaboration, and retention through realistic, risk-free practice.
What governance and scalability considerations should organizations address when deploying AR and VR breakthroughs at scale?
Key considerations include data privacy, consent, and ethical use of captured visuals and analytics, as well as interoperability and vendor neutrality. Organizations should plan for integration with ERP/MES/EHR, establish clear KPIs, and implement governance around data minimization and security to sustain adoption and maximize ROI.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What AR and VR are | AR overlays digital information onto the real world; VR creates immersive digital environments; breakthroughs bridge physical and digital worlds; expanding beyond labs to procurement, maintenance, and workforce development. |
| Technology backdrop and why it matters | Lightweight wearables enable day-long use; edge computing and 5G reduce latency for near real-time overlays; AI-driven analytics extract actionable insights from sensor data and maintenance records; enables precise, context-aware overlays. |
| AR applications in industry | AR-guided workflows in manufacturing and logistics reduce errors; field service with data streams and remote annotations; AR training and remote assistance shorten onboarding and aid safety; supports maintenance planning, inventory, and safety compliance. |
| VR breakthroughs in manufacturing and beyond | VR enables high-fidelity training, design reviews, and virtual prototyping; enables collaboration in shared virtual spaces; real-world examples include pilot training and healthcare simulations; supports scalable learning. |
| Industry transformations across sectors | AR guides assembly lines; VR accelerates design reviews and virtual commissioning; AR in healthcare; VR in education and training; field services with remote assistance. |
| Business models and workforce implications | Upskilling with AR training; ROI from reduced downtime and faster ramp-ups; device/software costs declining; governance and measurement of outcomes. |
| The human factor: changing skills and collaboration | AR/VR makes tacit knowledge explicit; improves safety and consistency; enhances collaboration with remote experts via real-time visuals and annotations. |
| Data privacy and ethics in AR/VR | Governance with access controls and data minimization; clear policies on visuals and telemetry; latency and reliability are critical in high-stakes environments. |
| Challenges and limitations to watch | Hardware costs, battery life, ergonomics; interoperability and standardization; ERP/MES/EHR integration; user acceptance and change management. |
| The path forward: strategic steps for organizations | Develop a clear business case with measurable outcomes; run pilots; phased AR-first then VR expansion; best practices: start small, flexible architecture, user-centric design, governance, KPIs. |
| The future of AR and VR in industry | More wearables, higher-fidelity simulations, smarter overlays; embed mixed reality into core processes to enable safer, smarter work; scalable learning from on-site knowledge. |
Summary
Augmented Reality and VR breakthroughs are transforming industries by turning immersive technologies from novelty into core drivers of productivity, safety, and innovation. They enable real-time guidance, safer training, and smarter collaboration across manufacturing, healthcare, education, and field services. As adoption grows, a clear business case, phased pilots, and governance are essential to realize measurable benefits such as reduced downtime, fewer errors, and faster time-to-market. The future of these technologies rests on thoughtful integration with existing systems and a culture of continuous learning.