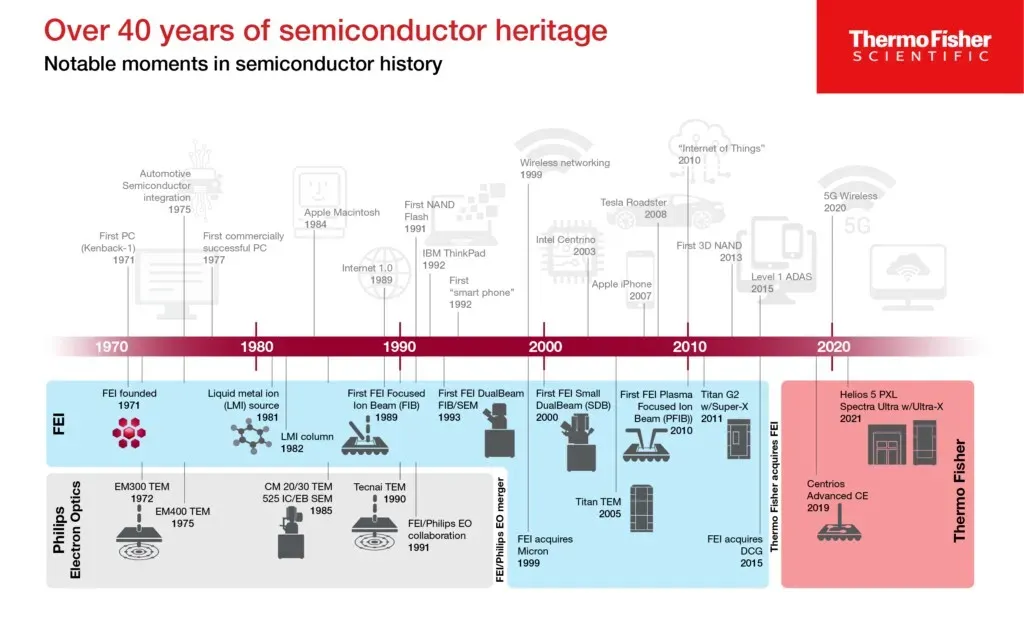
The Year in Semiconductors has arrived with notable leaps in performance, efficiency, and integration. As AI workloads expand, AI chips advancements are reshaping edge devices and data centers. Chiplet architecture and modular design are enabling faster time-to-market while keeping die sizes manageable. R&D efforts across the supply chain are pushing new process nodes and packaging strategies to balance capacity, yield, and reliability. Together, these forces signal a broader shift in how products are designed, sourced, and scaled across industries.
Beyond the introductory overview, the current semiconductor cycle highlights memory tech developments that underpin scalable AI and data workloads. Analysts describe the landscape as a modular, heterogenous ecosystem where providers optimize packaging, cooling, and bandwidth to extract maximum efficiency. As supply chains adapt, customers seek flexible platforms, standardized interfaces, and cross-vendor collaboration to accelerate product lifecycles. In practical terms, the year’s momentum translates into better edge devices, more capable servers, and automotive-grade reliability through tighter integration and smarter power management. Looking ahead, expect continued emphasis on scalable manufacturing and design strategies that enable rapid, cost-effective deployment.
Year in Semiconductors Spotlight: AI Chips Advancements and Efficiency
Across the Year in Semiconductors, AI chips advancements are redefining efficiency with domain-specific accelerators, tensor processing units, and architectures that optimize compute density and data movement. Vendors optimize memory bandwidth, on-die caches, and interconnects to balance training and inference workloads. Sparse matrix engines and neural processing units deliver energy-efficient performance for common AI tasks, enabling smarter edge devices and scalable data-center accelerators. Speed isn’t the only metric; memory usage and data movement efficiency are critical, as high-performance AI workloads stress bandwidth and latency budgets. This convergence shapes product design, time-to-market, and power envelopes across consumer electronics, automotive systems, and cloud infrastructure.
As AI workloads rise, the industry emphasizes smarter memory hierarchies and software toolchains that exploit high-bandwidth memory and low-precision computing. The interplay between AI chips advancements and software optimization accelerates practical speedups without exponential thermal penalties. For designers, this means more capable devices at lower energy per operation, with better performance per watt and more predictable performance under diverse inference tasks. The Year in Semiconductors thus frames a landscape where hardware specialization is tightly coupled with data-centric software strategies to deliver real-world impact.
Chiplet Architecture and Modular Design: A New Era of System-level Integration
Chiplet Architecture and Modular Design enable heterogenous integration by composing cores, accelerators, memory, and I/O within a single package. Standardized interposers and high-speed interconnects reduce die area and yield risk, while die-to-die communication protocols enable scalable performance without a monolithic die. This approach supports accelerated time-to-market, allowing best-in-class components from different vendors to be combined and upgraded over successive generations.
For product teams, chiplet architecture translates to more reliable supply chains and faster refresh cycles. Reusing proven blocks across products minimizes NREs and helps manage manufacturing risk. Packaging and system-level integration technologies—like SiP and advanced interposers—are essential to achieve low-latency, high-bandwidth connections between dies, unlocking new form factors in laptops, servers, and edge devices.
Foundry Innovations and Process Scaling: From EUV to 2nm and Beyond
Foundry innovations continue to push the envelope of process scaling and capacity. EUV lithography remains central to shrinking critical dimensions, while R&D moves toward 2nm and beyond to increase transistor density and reduce leakage. Beyond lithography, advanced packaging—2.5D and 3D stacking with high-bandwidth interconnects—enables chiplets to reach performance targets once reserved for monolithic designs. This combination expands satellite capacity, regional hubs, and diversified suppliers, contributing to more resilient supply chains.
For AI chips advancements and memory tech developments, the throughput and power benefits from new process nodes are amplified when paired with smarter packaging and die-to-die connectivity. Foundry pricing, yield management, and ramp timing are critical, as customers seek predictable lead times and cost efficiency. The result is a more flexible path to scaling performance while preserving reliability and manufacturability across varied product families.
Memory Tech Developments: From HBM to MRAM and ReRAM
Memory technologies are keeping pace with compute demands through 3D-stacked memory, high-bandwidth memory (HBM), and optimized DRAM interfaces. This memory tech developments trend is essential to feed AI accelerators with low-latency data paths and substantial bandwidth, reducing bottlenecks between compute units and off-chip memory. Designers increasingly favor integrated memory solutions and packaging strategies that bring memory closer to compute, enabling higher throughput and lower energy per bit.
Emerging non-volatile memories such as MRAM and ReRAM are gaining traction for specific workloads where endurance and density matter as much as speed. These technologies complement traditional DRAM by offering faster write endurance and near-zero standby power, enabling smarter caching, persistent accelerators, and robust edge devices. As memory capacity scales, awareness of timing, error correction, and thermal considerations becomes critical to maintain reliability in AI and data analytics workloads.
Packaging and Interconnects: Advancements in SiP, 2.5D/3D Integration
Packaging innovations and interconnects underpin the benefits of chiplet ecosystems. Advanced interposers, high-speed die-to-die links, and system-in-package (SiP) configurations connect multiple dies as a single, cohesive system. By reducing parasitics and improving thermal performance, these packaging breakthroughs enable higher bandwidth, lower latency, and more flexible upgrades without redesigning silicon. The result is stronger alignment with AI chips advancements and memory tech developments across a broad set of devices.
Effective packaging also supports better supply chain resilience by enabling modular upgrades and mass customization. Assembling multiple dies in a single package allows vendors to mix best-in-class components and optimize thermal budgets, while maintaining manufacturability across regional fabs. This packaging focus is essential to realize the full potential of chiplet architecture in laptops, data-center servers, automotive systems, and edge devices.
Manufacturing Trends and Supply Chain Resilience: Global Capacity and Risk Management
Manufacturing trends reflect a shift toward regional capacity, faster fabs, and smarter inventory controls to mitigate volatility in demand. Investments in new facilities, automation, and process monitoring are accelerating, while diversification of suppliers reduces single-source risk. This landscape is shaped by the need to support AI chips advancements and chiplet architectures with predictable ramp timing and quality.
Industry stakeholders are aligning on governance, standardization, and collaboration to strengthen the global pipeline. By embracing data-driven manufacturing, modular design, and robust logistics, the ecosystem can respond to surges in demand, supply shocks, and geopolitical considerations. The Year in Semiconductors thus becomes not just a timeline but a blueprint for resilient production and sustainable growth in memory tech developments, AI chips advancements, and the broader semiconductor market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What AI chips advancements defined this Year in Semiconductors?
The Year in Semiconductors highlights AI chips advancements such as domain-specific accelerators and tensor processing units that improve performance per watt. These architectures leverage high-bandwidth memory, low-precision computing, and innovative dataflow models to accelerate AI tasks in both edge devices and data centers while optimizing memory usage and data movement.
How does chiplet architecture influence product design in the Year in Semiconductors?
Chiplet architecture enables heterogeneous integration of cores, accelerators, memory, and I/O within modular packages. With standardized interposers and high-speed die-to-die interconnects, it lowers die area, reduces risk, speeds time-to-market, and improves yields, while allowing designers to mix best-in-class components across vendors.
What role did foundry innovations play in this Year in Semiconductors?
Foundry innovations drive capacity, yields, and new process nodes (including EUV and 2nm+) alongside advanced packaging (2.5D/3D, high-bandwidth interconnects). Regional hubs and diversified suppliers support resilience and predictable lead times, enabling AI chips advancements and memory tech developments across the ecosystem.
Which memory tech developments defined this Year in Semiconductors?
Memory technologies progressed with 3D-stacked memory and high-bandwidth memory (HBM), plus advanced DRAM interfaces. Momentum also grew for non-volatile memories like MRAM and ReRAM in targeted workloads, all aimed at reducing latency, increasing bandwidth, and enabling closer memory-to-compute integration.
How are manufacturing trends shaping the Year in Semiconductors?
Manufacturing trends emphasize regional capacity expansion, faster fabs, smarter inventory control, and stronger governance and standards. These shifts support resilience and faster ramp-ups for AI chips advancements and chiplet architectures while stabilizing the broader supply chain.
What practical takeaways does the Year in Semiconductors offer for product teams?
Key takeaways include embracing chiplet architecture for modular design, investing in advanced packaging and memory bandwidth, and aligning with foundry innovations and supply-chain strategies to improve time-to-market, scalability, and resilience in AI-centric and memory-intensive applications.
| Aspect | Key Points | Implications for Design & Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Forces Behind the Year in Semiconductors | Relentless demands for higher compute density, better power efficiency, and faster time-to-market; ongoing shift to heterogeneous computing; push beyond planar scaling via advanced packaging and chiplets. | Sets the stage for AI chips advancements, chiplet ecosystems, and memory tech to accelerate products with smarter data movement and modular supply chains. |
| AI Chips Advancements | Domain-specific accelerators and tensor processing units raise performance per watt; tuning memory bandwidth, on-die caches, and interconnects; architectures range from sparse matrix engines to neural processing units; use of high-bandwidth memory and low-precision compute. | Edge devices and data-center accelerators scale AI workloads with lower thermal envelopes; smarter memory management and closer software integration. |
| Chiplet Architecture and Modular Design | Heterogeneous integration combines cores, accelerators, memory, and I/O in one package; standardized interposers and high-speed interconnects; die-to-die protocols enable reuse of building blocks across products. | More flexibility, better yields, faster time-to-market via modular designs and staggered node adoption; resilient supply chains. |
| Foundry Innovations and Process Scaling | EUV lithography; ongoing moves to 2nm and beyond; advanced packaging (2.5D/3D); high-bandwidth interconnects and heterogeneous integration; regional hubs and diversified suppliers. | Predictable lead times; broader support for AI chips and memory; improved supply resilience. |
| Memory Technology Developments | 3D-stacked memory, advanced DRAM interfaces, HBM; MRAM and ReRAM for specific workloads; progress in reducing latency and energy per bit; denser, more resilient caches. | Memory bandwidth remains a bottleneck; integrated memory solutions and packaging bring memory closer to compute. |
| Packaging, Interconnects, and System-Level Integration | Chiplet-based packaging; advanced interposers; SiP; multi-die systems as a single platform; reduced parasitics and better thermal performance. | Enables higher bandwidth, more flexible supply chains, and easier upgrades without full silicon redesign. |
| Manufacturing Trends and Supply Chain Considerations | Regional capacity expansion; faster fabs; smarter inventory control; governance, standardization, and collaboration across designers, manufacturers, and suppliers. | Resilient ramp-ups and supply chain continuity for AI chips and chiplet ecosystems. |
| Market Implications and Industry Outlook | AI chips drive data center competitiveness; chiplet architectures enable faster product cycles and cost-effective upgrades; memory and packaging influence mobility, automotive, and enterprise segments. | Strategic alignment with modular designs, scalable manufacturing, and robust IP ecosystems. |
| Future Outlook: What to Expect Next | Continued scaling of packaging and integration; refinements in memory tech; deeper specialization of AI chips; closer collaboration among suppliers, cloud providers, OEMs; standards and interoperability. | A more resilient, capable, and adaptable semiconductor ecosystem prepared to meet growing demand. |
Summary
Year in Semiconductors captures a dynamic, multi-faceted view of how AI chips advancements, chiplet architecture, foundry innovations, memory technology developments, packaging, and manufacturing trends reshape devices and markets. This year’s progress shows how strategic choices in packaging, integration, and supply-chain planning influence product performance, energy efficiency, and time-to-market. For engineers, executives, and policymakers, staying informed about these trends is essential. By embracing modular designs, investing in advanced packaging, and prioritizing memory bandwidth alongside compute power, stakeholders can navigate the evolving terrain and help drive the next generation of semiconductors.